MCP Explained Part 4: REST API
The Blockscout MCP server’s REST API is a lightweight HTTP layer that reuses existing MCP tools, offering seamless access for systems that don’t natively support the Model Context Protocol.

TL;DR: The REST API in the Blockscout MCP Server is a thin HTTP layer built on top of the same tools available through MCP. It doesn’t duplicate business logic but provides an access method for systems that don’t natively support MCP.
MCP Explained - Index
Architecture
The REST interface was originally created for integration with the Higress Gateway, which allows MCP servers to run as wrappers around REST APIs (see Higress MCP plugin docs).
An MCP server running as a Higress plugin must support multiple blockchains while still respecting LLM context limitations (see Part 2: Optimizations).
Using the Blockscout API directly in this setup turned out to be impractical:
- A single plugin cannot easily describe paths to multiple Blockscout instances
- The Higress configuration language offers limited tools for transforming API responses into LLM-friendly outputs
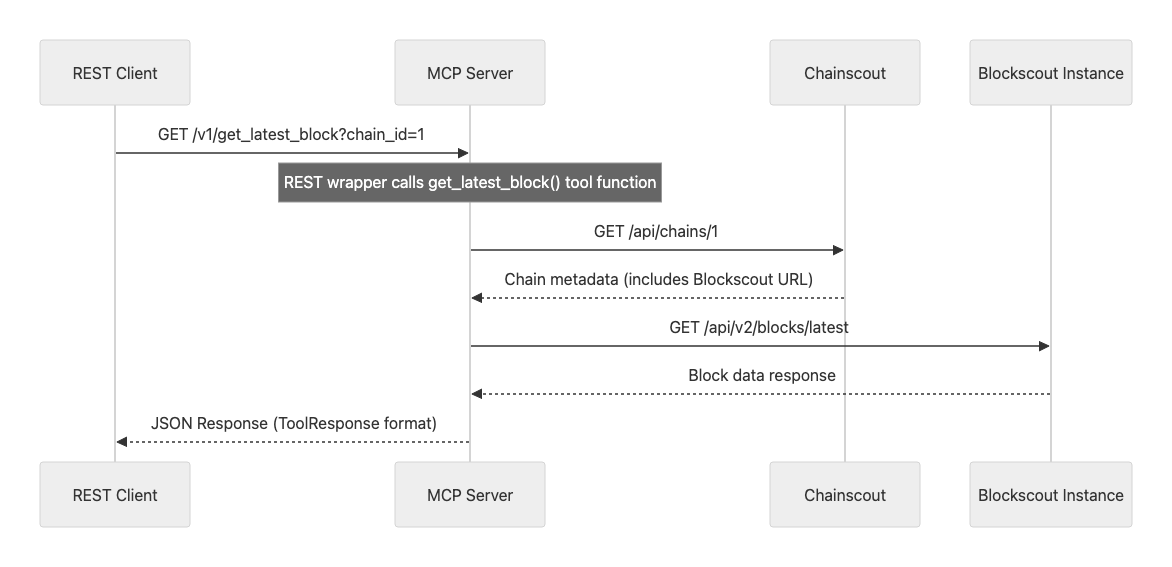
As a result, a REST interface was built as an AI-friendly wrapper over the optimized MCP logic. REST requests are processed by the same code as MCP tools: data is filtered, pagination handled contextually, and truncation or simplifications applied when needed.
Later, it became clear that the same endpoints work perfectly for creating a Custom GPT - Blockscout X-Ray - back when ChatGPT didn’t yet support direct MCP connections.
🤖 There's a new helper in ChatGP Town: Blockscout X-Ray
— Blockscout 🔭 (@blockscout) September 10, 2025
Your personal onchain analyst, hooked into Blockscout block explorers
Try it out here:https://t.co/fyGuJqNhbj
🧵 Or learn more about X-Ray in its own words: pic.twitter.com/UJyVN8AfPs
Standardized Response Format
REST endpoints return data in the same structure as MCP tools - the ToolResponse format. It separates meaningful data from auxiliary information:
{
"data": {...},
"notes": [...],
"instructions": [...],
"pagination": {...}
}
This format keeps behavior predictable for both LLM agents and traditional REST clients.
Errors are also unified:
{"error": "Error description"}
Thanks to this design, the server stays consistent and robust no matter how it’s accessed - through MCP or plain HTTP.
The same code processes requests from Claude.ai, IDEs, the Higress Plugin, or Custom GPTs, simplifying maintenance and avoiding any drift between interfaces.

